

International competitivenessĪ monopoly firm enjoys its power in its home country, but in some cases, firms face global competition. Developing medicines have a huge risk, but monopoly profits give sufficient support to take the risk. Therefore, it becomes an important part of many industries, for example, aircraft manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, telecommunication. There is a huge cost which is spent on research and development to keep the cost of the product effective. So, in this case, it is beneficial to have a low variable cost. industries like mineral water, steel production have a high fixed cost. The cost of production starts to decrease with the increase in the level of production, which makes the price of the product also lower and affordable for consumers. But, their supernormal profits in long The long- run equilibrium of a monopoly firm is illustrated in the graph below: Monopoly meaning in economics by Diagram/CurveĪdvantages of monopoly Economies of scale A monopoly firm will produce big amounts of goods at the lowest cost. In the situation of large market size and expansion. When there is no threat from new firms, a monopoly firm makes long-run adjustments in the plant’s scale. If the case new firm tries to enter the industry lowers ower down its prices goods to such an extent that a firm will start to incur losses. The firm might have a patent, or the market of the goods is limited. These entry barriers are because of control on raw materials used in the industry.

The monopoly industry has barriers to the entrance of new-firms into the market. Next topic in monopoly meaning in economic, the equilibrium point of monopoly firms in the long-run. Now, understand monopoly meaning in economic equilibrium in the long-run.
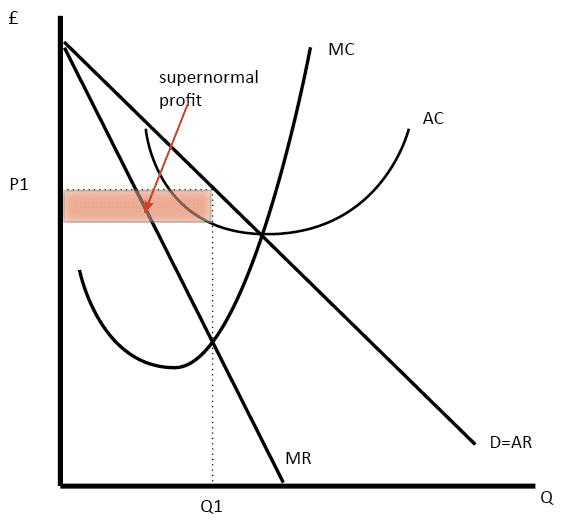
Short-run is a certain period in the future. Understands the levels of equilibrium in the short and long run the and type of profit firms can earn to elaborate monopoly meaning in economics. The equilibrium of the monopoly market is categorized into short-run and long-run. These five types of a monopoly market, which illustrates the monopoly meaning in economics. And, the industrial monopolies are created by statutory measures. That means these industries will have a public monopoly of the Central Government. This monopoly is created by the government by restricting privates sector entry in some industries For example, The Industrial Policy Resolution 1956, in India, restricts private industry involvement in some industries like arms and ammunition, atomic energy, railways. Industrial Monopolies or Public Monopolies It safeguards the interest and work of people. because of different laws in countries, nobody can copy the designs which are registered under one brand name, patent or trademark. The monopoly which emerged because of any legal provisions like copyrights, patents, trademarks etc is called a legal monopoly. This type of monopoly gives a different outlook to monopoly meaning in economics differently. This monopoly came naturally to these countries. Mica in India, nickel production in Canada are good examples of natural monopoly. There can be natural causes for establishing a monopoly market, this type of monopoly is called a natural monopoly. In an imperfect monopoly, a firm produces a product, with the presence of close substitutes in the market. It is a very rare monopoly.Īn imperfect monopoly firm has a limited degree of power. They enjoy more monopoly power as compare to another type of monopoly.Ī pure monopoly firm has absolute monopoly power. Monopoly firm which controls all the supply of products as well as related things such forms of market structure is called a pure monopoly. On the other hand, discriminating monopoly firms charge a different price for the same quantity from different consumer. Types of monopoly meaning in economics Simple Monopoly and Discriminating MonopolyĪ firm that is charging uniform or similar prices for its products and services is called a simple monopoly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
