

This is an energy-consuming process and the amount of energy required to separate these strands is directly proportional to the strength of the bonds. These are required for storage and transfer of information, repairing process, etc.įor replication of DNA first, the two strands are separated from each other and thereafter, complementary base pairs are added to form another copy of DNA. If the two strands are bonded through weak linkages such as Vander Wal forces it might lose some critical or vital information while passing from one generation to another.Īlso, we know that DNA molecules undergo a replication process through which multiple copies of DNA are formed. As DNA works as the hereditary material it is very important that it should be a stable structure. Hydrogen bonding actually plays a very crucial role inside a DNA molecule. This coiling and twisting of DNA make it rather more stable and less susceptible to changes in the outside environment.Īs we have already seen in the previous section the nitrogenous bases are bonded together through hydrogen bonds and these hydrogen bonds are responsible for holding the two strands of DNA together. one strand runs from 3’-5’ end while the other strand runs from 5’-3’ end. The two strands of DNA are coiled in a right-handed fashion and are anti-parallel to each other i.e. Essentially, purines bond with their opposite pyrimidines and vice versa. These bonds are responsible for binding the two strands of DNA molecule together thus making it stable.Īmongst these adenine and guanine are double ring structures and are called purines while thymine and cytosine are single ring structures and are classified as pyrimidines. As per Chargaff’s rule adenine always bonds with thymine through a double bond while guanine always bonds with cytosine through a triple bond. These bases bond with their complementary base present on the opposite strand of DNA through hydrogen bonds. The structure of nucleotides differs owing to the presence of four different types of nitrogenous bases viz. These sugar-phosphate bonds form the backbone of DNA molecules. Looking at the structure of a DNA strand it is observed that the phosphate group is attached to the hydroxyl group (5’) of one sugar molecule, forming an ester bond on its one side, and the 3’ carbon atom of the adjacent sugar molecule.Īs two ester bonds are formed through a phosphate link, this bond is termed phosphodiester linkage. Human genome consists of about 3,20,00,000,00 nucleotides.
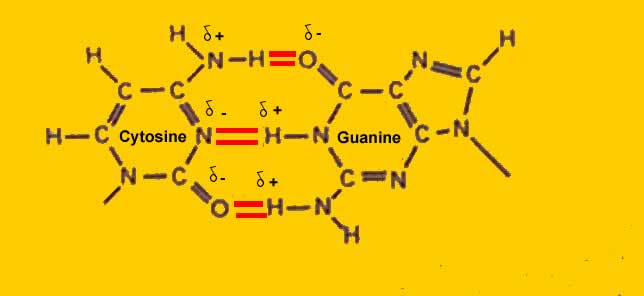
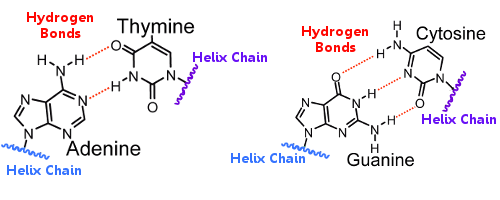
a deoxyribose sugar (pentose), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group.Ī large number of nucleotides bond together to form one strand of DNA. The two strands of DNA are composed of nucleotides and each nucleotide is a combination of three molecules viz. Let us study the bondings in DNA in detail.ĭNA is a double-stranded structure that serves as a carrier of biological information for most organisms. Therefore, multiple hydrogen bonds exist between the complementary nucleotides located on opposite strands of DNA. The adenine molecule forms a double bond with thymine while guanine forms a triple bond with cytosine. The purines always bond with pyrimidines, however, the number of bonds differs between the two types of base pairing. So, does DNA have hydrogen bonds? Yes, the two strands of the DNA molecules are joined through hydrogen bonds. However, another type of DNA called mitochondrial DNA which is maternally inherited is located in the mitochondria of the cell.Īn interesting question regarding bonds inside the DNA molecule is whether DNA consists of hydrogens bonds in it or not. Most DNA is located inside the nucleus of a cell. The different individuals, even when they belong to the same species do not have identical DNA except for the congenital twins that are born with the same DNA.ĭue to its uniqueness DNA also serves as a source of identification. It is responsible for the transmission of various traits from one generation to another.Įvery cell of the body contains its own DNA which is unique to every individual. Deoxyribonucleic acid, abbreviated as DNA is the hereditary material of almost all the living beings on earth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
