
But I am not sure why they use one not the others. Some examples of commands that use ESSID, BSSID or SSID as their arguments. Which one should apply to the wireless network created by my router in my apartment: ESSID, BSSID, or SSID? What differences are between usages of essid, bssid and ssid? When to use which? How can I tell if a wireless network has essid, bssid or ssid? ESSID and BSSID are just their IDs respectively.
Some access points have counter-measures against basic attacks like broadcast deauth, so you'll probably need to issue a deauth whilst impersonating the target connected client.You could be injecting on the wrong channel or radio band.Your interface is not injecting packets properly.Possible causes for the attack failing are:
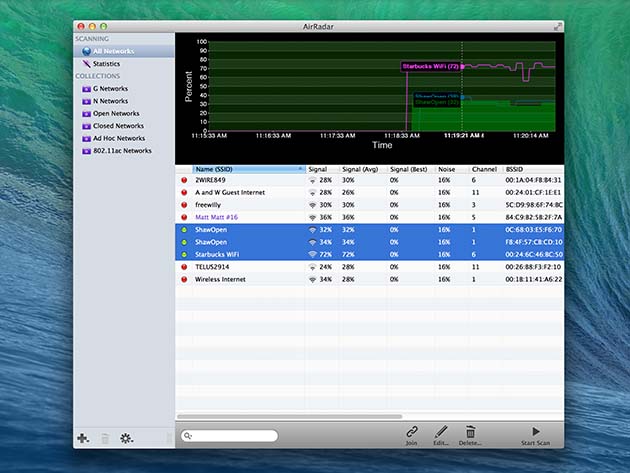
AIRRADAR BSSID MAC
Once associated and port scanning, what you are seeing is a kind of ethernet network and the base station presents itself as a layer 2 device with its own MAC address *:8C.įor your attack you should definitely target the correct BSSID, not the interface's MAC address. Notice that each radio on a base station is its own interface, so there could be multiple BSSIDs per SSID. What you observe on your wireless scanning and deauth attacks are BSSIDs which correspond to individual SSIDs, usually very similar to the interface's MAC address only incremented by one per SSID *:8D, *:8E. Whilst very similar, the base station's BSSID isn't the same as its MAC address. The only devices that seems to be vulnerable is a linux wifi printer which gives me 64/64 ACKs but i can't check easily if it's actually working. I tried to impersonalize another device using -s option but then I recive 0/64 ACKs while attacking computer or phones. Then I put the security measures of my router in "low mode" but the attack is failing again and again. I've check if I'm currently injecting packets correctly, using aireplay-ng -9 wlp3s0monĪnd the output says Injection is working! There's a way to perform the attack on the correct BSSID? Using the channel 1 for the attack (the same attack works with 8D and channel set on 1).
This is what I used for the attack: aireplay-ng -0 0 -a 10:13:31:F1:48:8C wlp3s0monĪnd the result is: 00:03:55 Waiting for beacon frame(BSSID 10:13:31:F1:48:8C) on channel 1 So I tried to perform the attack on the 8C BSSID manually (because it is not detected by airodump-ng) but the attack fails. Then I ran Zenmap from inside of the network to check if my router's BSSID was correct and I found that all the devices connected to wifi shown a different BSSID for the router, which is: 10:13:31:F1:48:8C: the difference is in the last digit. When i put my wireless interface in monitor mode to scan the network from the outside I found the router's BSSID, which is 10:13:31:F1:48:8D, and then I tried to perform various deauthentication attacks on the network but all of them failed: my computer can successfully send packets but the network is not affected (since my other devices can access internet normally). I'm using airgeddon ( ) to perform a deauthentication attack on my wifi network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
